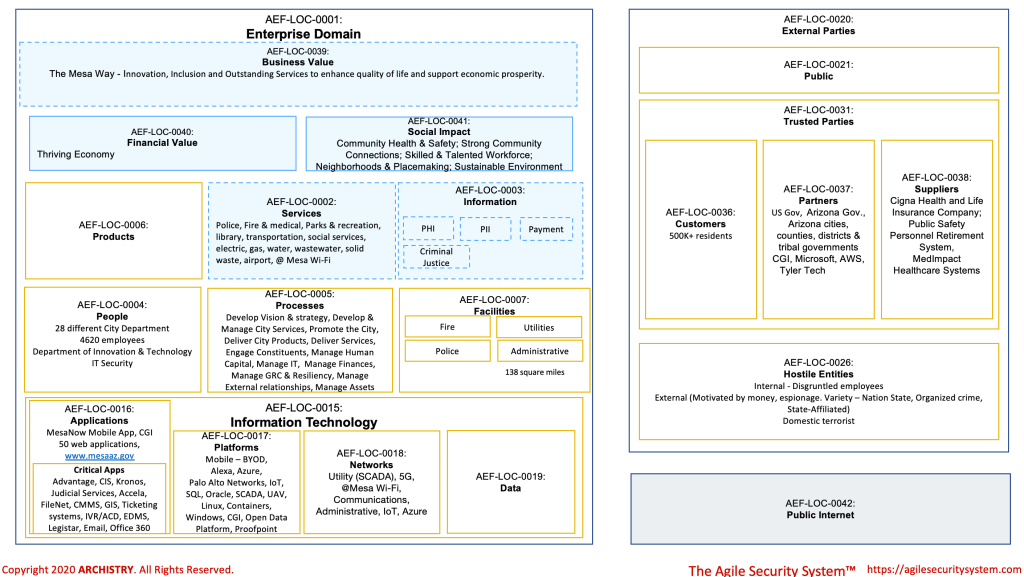
Presented here is another segment in the series focusing on constructing a business contextual architecture, utilizing the Agile Security System devised by Andrew Townley. This particular case study centers on the public sector, specifically examining the context of the City of Mesa, Arizona. The figure below is the Domain Impact Worksheet from the Agile Security System.
Methodology
Please note that I use the phrases of “security objectives” or “business objectives” throughout the observations below. This is an architectural or strategy technique that I learned from SABSA and Andrew Townley. SABSA refers to them as “business attributes.” Business attributes are abstractions of risk mitigation strategies or enablement strategies that must be met for an organization to deliver or achieve a desired outcome, goal or objective. The specific security objectives, like Available, Risk-Managed, and associated definitions are from “Getting Started with the Agile Security System” (Townley, 2023, Appendices E and F). A cybersecurity strategy and operations need to incorporate and deliver on these cybersecurity objectives.
Observations
- The official website, www.mesaaz.gov, stands as the primary brand for the City. Residents depend on the site’s continuous availability, anticipating unfettered access at all times. Moreover, residents expect that any information gathered from them is handled with the utmost protection. The security objectives, encompassing Availability, Governed, Duty-Segregated, Reputable, and Safe, are paramount in this context. Additionally, Customer-focused, Usable, and Resourced are other important business objectives.
- Data.mesaaz.gov and openbudget.mesaaz.gov assume a pivotal role in promoting the City’s strategic priority of cultivating “Strong Community Connections.” The essence of their importance is rooted in harnessing data analytics, minimizing disruptions to stakeholders, and aligning with the objective of ensuring transparency with citizens, thereby helping the implementation of a smarter Mesa. These two websites share the same security objectives as www.mesaaz.gov, including Availability, Governed, Duty-Segregated, Reputable, and Safe. Additionally, an overarching objective for Data.mesaaz.gov and openbudget.mesaaz.gov is to be Interoperable.
- Complexity and diversity of City Services are unapparelled. The City of Mesa operates utilities, medical service, police, transportation, library, parks, social services and public Wi-Fi. These services are delivered by people operating in 28 diverse departments within the City of Mesa. The services are structured by unique and overlapping processes and expose different types of information to customers and employees. The intricate complexity and diversity of services provided by the City of Mesa give rise to distinct business requirements, legislative demands, and a varied landscape of attack surfaces that require targeted risk mitigation strategies. A notable example is the existence of 52 internet-accessible web applications supporting diverse city processes. Consequently, it is imperative to incorporate critical security objectives into the cybersecurity strategy to effectively address these challenges. The essential security objectives include Risk-managed, Compliant, Documented, Recoverable, Access Controlled, Compliant, Integrity-Assured.
- Given the complexity and diversity of the City of Mesa’s services, the maturing of an Enterprise Architecture (EA) capability becomes imperative. The City has recognized the importance of maturing such capability by incorporating it into their IT Strategic Plan and Roadmap document. EA capability needs to incorporate and be integrated with Cybersecurity Architecture and Solution Architecture These architecture domains play a crucial role in ensuring that solutions are not only technologically sound but also aligned with key cybersecurity objectives and requirements. Customer-Focused and Governed are key business objectives. Enterprise Architecture can help break down silos, down silos, explore new technologies / capabilities, ensure IT alignment with the 50 year plan (see https://plan.konveio.com/tomorrows-mesa-2050-general-plan), and IT governance.
- Effective risk management and policy governance are indispensable for municipalities like the City of Mesa, particularly in the context of limited funding for cybersecurity compared to federal governments or private corporations. Prioritizing IT security and privacy funding via risk management is paramount. A key facet of risk management involves identifying the appropriate owner / role, whether it be a City Manager, Mayor, or Department Head, to accept, mitigate, or transfer risks. The integration of risk management with a comprehensive City-wide framework, beyond cybersecurity and privacy, is essential. The adoption of a “Domain Framework” based on SABSA becomes instrumental, where each domain is owned by an accountable individual responsible for setting policies and risk appetite, while adhering to the parent risk parameters and policies. For example, the City of Mesa via the Mayor and City Council would set a city wide risk appetite level and general cybersecurity risk policy (i.e., Enterprise Domain). All child domains (e.g. Process, Information, Information Technology) would have to adhere to the risk appetite and policies of the parent (i.e., Enterprise Domain). This approach enables the appropriate role to make and own risk decisions similar to the ones they are already making in finance, legal, and HR. Cybersecurity would need to be consulted on cybersecurity policy and risk decisions. This approach also removes IT Security as the perceived owner of all cybersecurity risk and a blocker to projects/initiatives. Cybersecurity could also work with domain owners to draft policies. Domain owners would be accountable for writing policies for their domain and demonstrating compliance to them.
- Cybersecurity in local governments is a public safety risk that needs to be Risk-managed and Safe.
- There are a lot of processes needed to structure the diverse City services. Process information in the Domain Impact worksheet are from the Process Classification Framework® (PCF), The City Government PCF. There is a potential opportunity to leverage the City Government PCF to benchmark services, resulting in improvements in processes and services. Per APQC, the PCF Experience serves as a high-level, industry-neutral enterprise process model that allows organizations to see their business processes from a cross-industry viewpoint.
- The City exhibits a seemingly greater transparency in sharing information about its IT assets compared to the private sector, evident in instances such as Palo Alto Networks customer success story featuring their technology used by the City. However, this abundance of information poses potential risks as threat actors could leverage it for reconnaissance purposes (see MITRE ATT&CK framework T1589, T1590, T1591). Therefore, a well-rounded cybersecurity strategy needs to incorporate the cybersecurity objectives of Educated, Classified, and Risk-Managed. Striking a balance between transparency and security is crucial to maintain the City’s resilience against potential cyber threats.
- The City of Mesa must allocate sufficient resources, if not already, to effectively identify and manage regulatory requirements for its complex environment. This necessitates collaboration, potentially through a committee comprising representatives from IT Security & Risk, the City Attorney’s office, and designated “Domain Owners” (see #5 above) for specific services. Any cybersecurity strategy needs to incorporate the objective of “Compliant.” Below are examples of potential regulatory and standards that may impose requirements for cybersecurity and privacy based on the information utilized and services offered by the City of Mesa. These sources should be carefully considered and integrated into the security strategy to maintain compliance: a) PHI – Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act; b) PII – Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act, The Electronic Communications Privacy Act, Arizona’s Data-Breach Notification Law; c) Payment Information – The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard; d) Water Utility – US Environmental Protection Agency Cybersecurity Checklist; e) Arizona Freedom of Information Act; f) US Transportation Security Administration cybersecurity requirements for airports and aircraft operators; g) US Executive Branch Strategies and Orders – National Cybersecurity Strategy, Executive Order 14028, Executive Order 13800. Policy Directive PPD-21; h) US Federal Aviation Agency’s regulations for Unmanned Aircraft System; i)NIST Cybersecurity Framework; j) Criminal Justice Information – FBI’s CJIS Security Policy; k) Cybersecurity Incident – SEC Rules on “Cybersecurity Risk Management, Strategy, Governance, and Incident Disclosure by Public Companies.” Obviously, the City of Mesa is not a publicly traded company and these rules don’t apply to the City. However, it might be worthwhile to adopt the SEC framework for handling disclosures in the spirit of transparency if it doesn’t conflict with other laws or regulations.
- Ransomware is a critical concern. Per the Verizon Data Breach report from 2023, ransomware remains the favored approach for disrupting government operations. Several security objectives need to be addressed in response to ransomware: Risk-Managed, Recoverable, Access Controlled, Integrity-Assured, and Educated. Dallas (May 2023 – June 2023) and City of Oakland (February – April 2023) are two examples cities impacted by ransomware attacks. At minimum, the City should, if not already: a) utilize the domain impact worksheet (or similar business architecture modeling or business impact analysis) to initiate the identification of critical services necessitating protection, resilience, and expedited recovery in the event of a ransomware attack; b) evaluate the City’s alignment with CISA’s Stop Ransomware Guide, potentially converting the guidance into a spreadsheet or web application to assess and monitor progress. This evaluation should encompass technology, personnel, and processes; c) encourage cybersecurity technology partners to conduct complimentary ransomware health checks and remediation assessments of their technologies deployed within the City of Mesa’s environment; d) ensure the existence of an up-to-date and tested Incident Response plan, involving key stakeholders such as the City Manager, City Attorney, Mayor, and Councilors. Additionally, safeguard and regularly test the backup and restore infrastructure to ensure its effectiveness in mitigating the impact of a potential ransomware incident. Ensure there is reputable incident response company, like Verizon, Mandiant etc, on retainer to assist with incident response along with appropriate federal and state agencies.
- The City of Mesa should be cognizant of several trends identified in the 2023 Verizon Data Breach Report that are relevant to its security posture. While the report does not provide a breakdown for government levels, the patterns observed, such as system intrusion, basic web attacks, DDoS, social engineering, and miscellaneous errors, are pertinent to municipal entities. Espionage-motivated actors pose a notable threat in this sector, and the persistent issue of collusion between disgruntled internal actors and external entities requires attention. Financially motivated actors and nation states targeting public sectors for information remain a concern, with personal information being the most frequently stolen data type. In response to these threat actors, critical security objectives, including Risk-Managed, Integrity-Assured, and Risk-Aware, must be addressed. The City of Mesa should explore the feasibility of implementing geo-blocking for all web applications, except www.mesaaz.gov, to ensure it continues to support efforts to market and attract individuals and organizations to the city. Additionally, it is advisable for the city to assess its control maturity and capabilities against recognized frameworks such as the CIS Critical Controls and MITRE ATT&CK to ensure a robust and adaptive security posture, especially for applications listed in the “Critical Apps” subdomain. Side note – I like that VERIS has mapped their incident classification patterns to MITRE ATT&CK framework techniques and the CIS Critical Controls
- Similar to other cities, the City of Mesa has placed a strategic emphasis on evolving into a “Smarter City.” As the city progresses towards becoming smarter, several of the previously mentioned Security Objectives remain applicable. The criticality and frequency of cybersecurity incidents are expected to rise, especially as services increasingly rely on interconnected Operational Technology (OT) systems, Information Technology (IT) systems, and Smart City infrastructure. Recognizing the growing complexity and interconnectivity, CISA has offered cybersecurity best practices tailored for and attributes of a trusted for Smart Cities. Consulting and potentially adhering to these best practices is crucial for the City of Mesa to enhance the security posture of its Smart City initiatives.
- Like Rogers Corporation, the City of Mesa has a cloud presence. I would have the same observations for the City of Mesa as those for Rogers Corporation.
Initial questions
- Is the accuracy of the Domain Impact worksheet accurate, or are there crucial elements missing?
- What are critical services and initiatives requiring guidance from cybersecurity?
- What is the risk management process for identity, assessing, addressing etc. risk?
- Who is responsible for collecting regulations etc. and converting them into policies and requirements?
- Is there a dedicated cybersecurity and IT plan for managing attacks involving ransomware?
- Why is business continuity with Cybersecurity?
- How are cybersecurity items on the IT Strategy and Roadmap identified and prioritized?
- How does cybersecurity architecture, enterprise and solution architecture integrate?
- What components of the CIS Critical Security Controls are in place for the Information Technology parent domain in terms of people, process and technology?
- How is the cloud governed? Are there any initiatives involving cloud?
- How is the network segmented?
- How mature is City of Mesa’s Security Operations Capability?
